Introduction to JavaScript SEO
JavaScript powers the dynamic, interactive web experiences of 2025, enabling features like single-page applications (SPAs), infinite scrolling, and real-time content updates. However, its reliance on client-side rendering introduces unique challenges for search engine optimization (SEO). JavaScript SEO focuses on ensuring search engines, particularly Google, can crawl, render, and index JavaScript-generated content effectively. This is critical because Googlebot processes pages in stages—crawling raw HTML, rendering JavaScript to form the Document Object Model (DOM), and indexing the final output.
Entities like Googlebot, rendering pipelines, and client-side rendering (CSR) are central to this process. Without proper optimization, JavaScript-heavy sites risk poor SERP visibility, reduced organic traffic, and missed opportunities. For example, content loaded dynamically via JavaScript may not be indexed if it’s not accessible in the initial HTML response. As search queries increasingly demand dynamic content discoverability, mastering JavaScript SEO is essential for aligning with user intent and building topical authority in web development and technical SEO.
This 3,000-word guide provides a detailed, actionable approach to implementing JavaScript SEO best practices. Drawing from authoritative sources like Google’s Webmaster Guidelines, we’ll explore challenges, strategies, tools, real-world examples, and emerging trends. Whether you’re optimizing a React-based SPA or a Next.js site, these techniques will enhance your site’s performance in an AI-driven search landscape.
Understanding JavaScript and Its Role in SEO
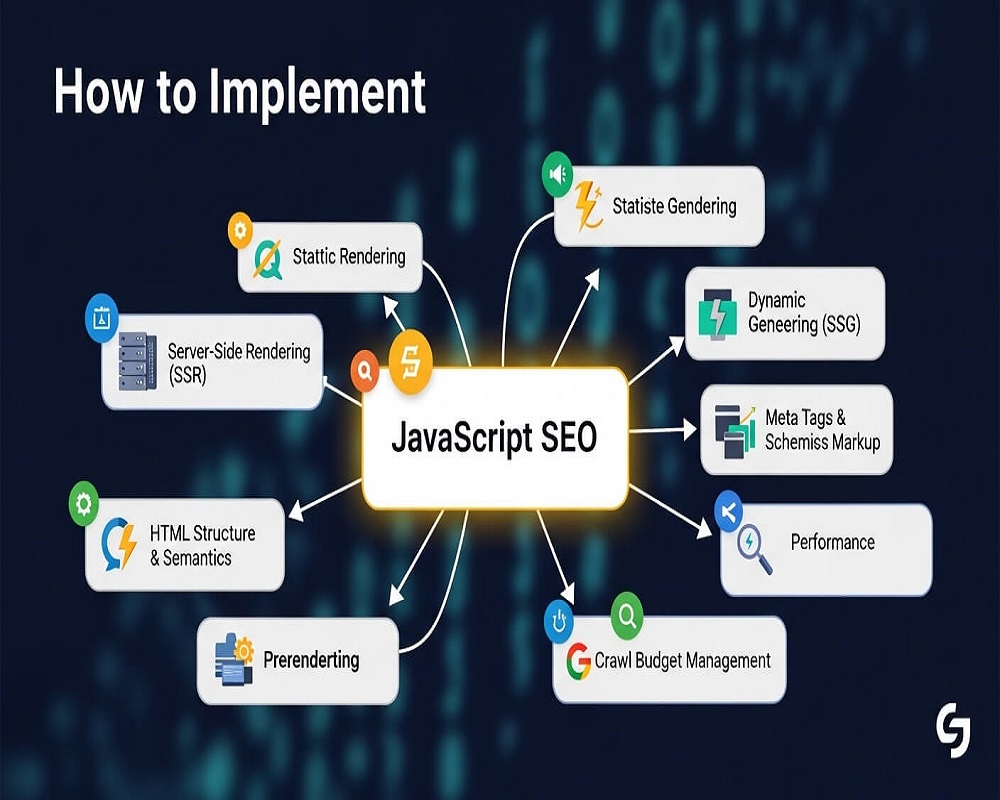
JavaScript is a scripting language that manipulates the DOM to create interactive web experiences without full page reloads. In SEO, it interacts with entities like crawl budgets, rendering queues, and indexing signals. Google uses a headless Chromium browser to execute JavaScript, but not all crawlers (e.g., Bing or AI-driven bots) fully process it, creating potential visibility gaps.
Key concepts include:
- Client-Side Rendering (CSR): Content renders in the browser, which can delay indexing if Googlebot queues pages for later rendering.
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Pre-rendered HTML is sent from the server, enabling faster crawling and indexing.
- Static Site Generation (SSG): Pages are built at compile time, ideal for static content.
- Hydration: Adds interactivity to pre-rendered HTML, balancing SEO and user experience.
Semantically, these concepts tie to user queries like “how to make dynamic sites rank higher,” which relate to Core Web Vitals (CWV) such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP). Optimizing JavaScript ensures alignment with Google’s focus on accessible, user-centric content, enhancing discoverability for both search engines and users.
Challenges with JavaScript in SEO
JavaScript introduces several obstacles in the crawl-render-index process:
- Crawling Limitations: Googlebot may miss links or content injected via JavaScript if they’re absent from initial HTML. Blocked .js files in robots.txt worsen this issue.
- Rendering Delays: Heavy JavaScript bundles or external dependencies can queue pages in Google’s rendering system, delaying indexing by days or weeks.
- Indexing Issues: Content hidden behind interactions (e.g., tabs, modals) or lazy-loaded without proper signals may not be indexed.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Large JavaScript files slow page load times, negatively impacting CWV and rankings.
- Non-Google Crawler Compatibility: Many AI or social media crawlers don’t execute JavaScript, limiting visibility in alternative search platforms.
These challenges connect semantically to topics like technical debt in web development and the need for hybrid rendering solutions, critical for addressing user intent around fast, discoverable websites.
Best Practices for JavaScript SEO
To overcome these hurdles, implement the following best practices, focusing on entities like HTTP status codes, meta tags, and structured data:
1. Adopt Server-Side or Hybrid Rendering
Shift from CSR to SSR or SSG using frameworks like Next.js or Nuxt.js to deliver fully formed HTML. This reduces reliance on Googlebot’s rendering queue.
- Implementation Tip: In Next.js, use
getServerSidePropsfor dynamic data orgetStaticPropsfor static pages to ensure content is crawlable.
2. Optimize Internal Linking and Navigation
Use standard <a href=""> tags for links instead of onclick events. Ensure navigation menus are in initial HTML for discoverability.
- For SPAs, implement the History API to manage URL changes without hash fragments (#).
3. Ensure Consistent Meta Tags
Include title, meta description, canonical, and robots tags in server-rendered HTML. Avoid JavaScript overwrites that could confuse crawlers.
4. Implement Proper Lazy Loading
Apply loading="lazy" to images below the fold, but ensure critical above-the-fold content loads immediately to avoid indexing delays.
5. Handle HTTP Status Codes Correctly
Return accurate codes (e.g., 404 for missing pages). In SPAs, use noindex meta tags for soft 404s or redirect to valid pages.
6. Incorporate Structured Data
Dynamically generate JSON-LD with JavaScript, but verify it renders correctly for rich results eligibility.
7. Enhance Accessibility
Use polyfills for older browsers and test with JavaScript disabled to ensure core content remains accessible.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing JavaScript SEO
Follow this structured process to optimize your JavaScript site:
Step 1: Audit Your JavaScript Setup
- Use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool to compare live vs. indexed page views, identifying rendering issues.
- Crawl your site with Screaming Frog or Sitebulb in JavaScript mode to detect discrepancies between raw and rendered HTML.
Step 2: Select a Rendering Strategy
- For new projects, adopt SSR with Next.js: Run
npx create-next-appand configure pages with export functions likegetServerSideProps. - For existing CSR sites, implement hydration to pre-render static content and add interactivity post-load.
Step 3: Optimize JavaScript Code
- Minify and bundle scripts using Webpack or Vite to reduce file size.
- Defer non-critical scripts:
<script defer src="script.js"></script>. - Ensure .js and .css files are not blocked in robots.txt.
Step 4: Enhance Content Discoverability
- Create content clusters around related entities (e.g., “JavaScript frameworks” linking to “React SEO strategies”).
- Submit an updated XML sitemap with all crawlable URLs.
Step 5: Test Rendering and Performance
- Run Lighthouse audits to assess CWV and JavaScript performance.
- Use Search Console to monitor metrics like LCP and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
Step 6: Monitor and Iterate
- Analyze GSC data for impressions, clicks, and CTR to refine JavaScript elements.
- A/B test changes to navigation or content loading strategies.
Tools and Technologies for JavaScript SEO
Leverage these tools to streamline implementation:
- Google Search Console: Identifies rendering errors and indexing status.
- Screaming Frog: Compares raw vs. rendered HTML for discrepancies.
- Sitebulb: Highlights JavaScript-specific issues like modified meta tags.
- Prerender.io: Serves pre-rendered HTML to bots for dynamic sites.
- JetOctopus JS Tool: Analyzes JavaScript impact on titles and load times.
- Lighthouse: Audits performance and SEO metrics.
- Frameworks: Next.js for SSR/SSG, Gatsby for static sites.
These tools strengthen topical authority by analyzing semantic elements like DOM changes and performance signals.
Common Mistakes in JavaScript SEO and How to Avoid Them
Steer clear of these pitfalls:
- Blocking Resources: Allow .js and .css in robots.txt; test with URL Inspection.
- Non-HTML Links: Use
<a>tags for navigation. - Hash-Based URLs: Switch to static paths with History API.
- JavaScript Redirects: Implement server-side 301 redirects.
- Hidden Content in Tabs: Expose critical content in initial HTML.
- Over-Reliance on Dynamic Rendering: Prioritize universal SSR for scalability.
- Large JavaScript Bundles: Minify and defer to improve load times.
Real-World Examples of JavaScript SEO Success
- HubSpot’s Next.js Transition: Migrated to SSR, improving indexation and boosting organic traffic by 40%.
- E-commerce Retailer: Optimized lazy loading for product images, enhancing LCP and increasing conversions by 15%.
- News Site: Used prerendering for JavaScript-heavy articles, reducing rendering delays and improving SERP rankings.
High-Volume Questions About JavaScript SEO
1.What Is JavaScript SEO and Why Is It Important?
JavaScript SEO ensures dynamic content is crawlable and indexable, vital for visibility in 2025’s AI-driven search environment.
2.How Does Google Process JavaScript for SEO?
Googlebot crawls HTML, queues for rendering with Chromium, and indexes the result. Delays occur with complex JavaScript.
3.Do JavaScript Issues Impact SEO Rankings?
Yes, they can delay indexing, harm CWV, and lower rankings due to poor user experience signals.
4.What’s the Difference Between CSR, SSR, and SSG for SEO?
CSR delays indexing; SSR and SSG deliver pre-rendered HTML for faster crawling and indexing.
5.How Can Single-Page Applications Be Optimized for SEO?
Use SSR, History API, and prerendering to ensure content accessibility.
6.Do All Search Engines Handle JavaScript Like Google?
No, many AI and social media crawlers don’t execute JavaScript, necessitating static fallbacks.
7.How Do I Test JavaScript Rendering for SEO?
Use Google’s URL Inspection Tool to compare source vs. rendered HTML and identify issues.
8.What’s the Role of Lazy Loading in JavaScript SEO?
It speeds up page loads but must not delay critical content to ensure indexing.
9.How Does JavaScript SEO Relate to Mobile-First Indexing?
Optimize for mobile by ensuring menus and content render without JavaScript dependencies.
10.Is Dynamic Rendering Still Effective in 2025?
Yes, but hybrid SSR is preferred for scalability and universal compatibility.
The Future of JavaScript SEO
As of September 23, 2025, JavaScript SEO is evolving with trends like edge-side rendering, AI-optimized code bundles, and zero-JS fallbacks for accessibility. Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and advancements in MUM emphasize real-time rendering and multimodal content. Future-proof your strategy by staying aligned with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and testing for emerging crawler capabilities.
Conclusion
Implementing JavaScript SEO best practices ensures your dynamic site remains discoverable and competitive. By prioritizing rendering strategies, optimizing code, and leveraging robust tools, you align with semantic user intent and establish authority in technical SEO. Begin with a site audit, apply these techniques, and monitor performance to thrive in 2025’s search landscape.
Saad Raza is an SEO specialist with 7+ years of experience in driving organic growth and improving search rankings. Skilled in data-driven strategies, keyword research, content optimization, and technical SEO, he helps businesses boost online visibility and achieve sustainable results. Passionate about staying ahead of industry trends, Saad delivers measurable success for his clients.