Factors of Numbers from 1 to 100
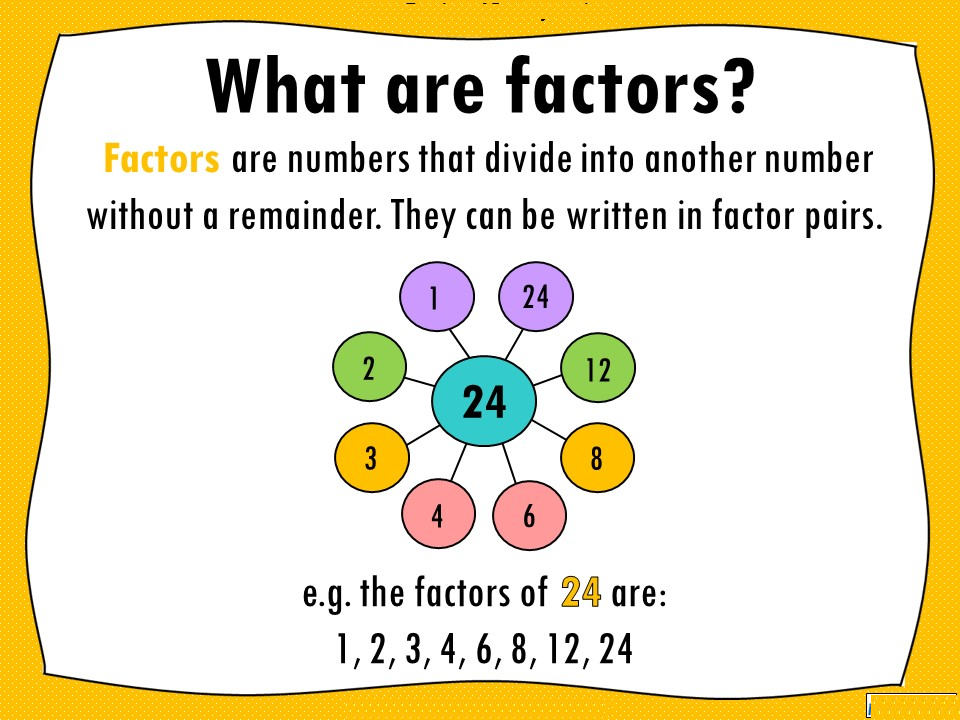
In mathematics, factors are the numbers that divide evenly into a given number. For example, the factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3, and 6 because all these numbers divide 6 without leaving a remainder. Understanding the factors of numbers is an essential concept in number theory, and it can be helpful in simplifying mathematical problems, finding greatest common divisors, and solving algebraic expressions. In this article, we will explore the factors of numbers from 1 to 100.
The Importance of Factors in Mathematics
In mathematics, the concept of factors is deeply intertwined with several key principles that form the foundation for many mathematical operations and real-world applications. Factors are not just useful for basic arithmetic; they play a crucial role in advanced topics like number theory, algebra, and geometry. Let’s delve deeper into why factors are important and how they influence our understanding of numbers.
Factors and Prime Numbers
One of the most critical areas where factors come into play is in the study of prime numbers. A prime number is a number that only has two factors: 1 and itself. Prime numbers are fundamental to mathematics because they are the building blocks of all integers. Every positive integer greater than 1 can be expressed as a product of prime numbers, a concept known as prime factorization.
For instance, the number 30 can be factored into prime numbers as: 30=2×3×530 = 2 \times 3 \times 5 This process of breaking down a number into its prime factors is a cornerstone of many algorithms, especially in fields like cryptography, where large prime numbers are used for secure communication.
Factors and Divisibility Rules
Understanding the factors of numbers is essential when working with divisibility rules. These rules allow us to determine whether one number is divisible by another without performing long division. For example, knowing that 10 is divisible by 2, 5, and 10 allows us to quickly check divisibility in many arithmetic problems. Similarly, divisibility rules help when simplifying fractions or performing mental calculations.
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The concept of greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM) relies heavily on understanding the factors of numbers.
- The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides each of them exactly, which can be found by examining their common factors. For example, the GCD of 36 and 60 is 12, as 12 is the largest number that divides both 36 and 60 without leaving a remainder.
- The LCM, on the other hand, is the smallest number that is a multiple of both numbers. It can be determined by finding the prime factors of both numbers, and then using the highest powers of each prime factor. For example, the LCM of 6 and 8 is 24 because 24 is the smallest number that both 6 and 8 can divide evenly.
These concepts are not only central in elementary mathematics but also in applications such as scheduling, event planning, and even in determining optimal resources in various fields like logistics and operations research.
Applications in Fractions
Another area where factors are crucial is in simplifying and comparing fractions. When we simplify a fraction, we find the common factors of the numerator and denominator and divide them by their greatest common divisor (GCD). This makes the fraction as simple as possible. For example, the fraction 16/24 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their GCD, which is 8:
Factorization in Algebra
In algebra, factorization is the process of writing an expression as the product of its factors. This process is crucial for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and analyzing polynomials. For example, the quadratic equation x2−5x+6x^2 – 5x + 6 can be factored into (x−2)(x−3)(x – 2)(x – 3), making it easier to solve or analyze. Factorization is a vital tool in solving systems of equations, expanding or simplifying algebraic expressions, and working with higher-degree polynomials.
Factors in Geometry
While factors are often associated with numbers, they also have applications in geometry. For instance, when calculating the area of geometric shapes like rectangles or triangles, we use factors to break down larger areas into smaller, more manageable sections. In certain problems involving the area of polygons, we can factorize the sides or dimensions to simplify the calculation.
Moreover, in geometry, understanding factors helps with scaling. For example, if the dimensions of a shape are scaled by a factor of 2, its area increases by a factor of 4, and its volume increases by a factor of 8. These relationships play a significant role in understanding how objects and shapes change when their size is altered.
Factors in Real-World Problems
Beyond the abstract mathematical world, factors play an essential role in solving real-world problems. Here are a few examples:
-
Cryptography: As mentioned earlier, prime factorization is the backbone of many encryption algorithms, especially in public-key cryptography. Security systems like RSA rely on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers.
-
Computer Science: Factors are used in algorithms for searching, sorting, and data compression. Efficiently identifying factors can speed up these algorithms, making them more practical for large datasets.
-
Engineering: In engineering, factors help optimize design. For example, factors are used in determining the stress and load on materials, optimizing the layout of systems, and finding the most efficient arrangement of components.
-
Economics and Finance: Factors are used in interest calculations, especially when working with compound interest and amortization schedules. Understanding the factors involved in these calculations helps in making financial decisions like loans, savings, and investments.
Factors of 1 to 10
- Factors of 1: The only factor of 1 is 1 itself.
- Factors of 2: The factors of 2 are 1 and 2.
- Factors of 3: The factors of 3 are 1 and 3.
- Factors of 4: The factors of 4 are 1, 2, and 4.
- Factors of 5: The factors of 5 are 1 and 5.
- Factors of 6: The factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3, and 6.
- Factors of 7: The factors of 7 are 1 and 7.
- Factors of 8: The factors of 8 are 1, 2, 4, and 8.
- Factors of 9: The factors of 9 are 1, 3, and 9.
- Factors of 10: The factors of 10 are 1, 2, 5, and 10.
Factors of Numbers 11 to 20
- Factors of 11: The factors of 11 are 1 and 11.
- Factors of 12: The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
- Factors of 13: The factors of 13 are 1 and 13.
- Factors of 14: The factors of 14 are 1, 2, 7, and 14.
- Factors of 15: The factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5, and 15.
- Factors of 16: The factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16.
- Factors of 17: The factors of 17 are 1 and 17.
- Factors of 18: The factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18.
- Factors of 19: The factors of 19 are 1 and 19.
- Factors of 20: The factors of 20 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, and 20.
Factors of Numbers 21 to 30
- Factors of 21: The factors of 21 are 1, 3, 7, and 21.
- Factors of 22: The factors of 22 are 1, 2, 11, and 22.
- Factors of 23: The factors of 23 are 1 and 23.
- Factors of 24: The factors of 24 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24.
- Factors of 25: The factors of 25 are 1, 5, and 25.
- Factors of 26: The factors of 26 are 1, 2, 13, and 26.
- Factors of 27: The factors of 27 are 1, 3, 9, and 27.
- Factors of 28: The factors of 28 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, and 28.
- Factors of 29: The factors of 29 are 1 and 29.
- Factors of 30: The factors of 30 are 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, and 30.
Factors of Numbers 31 to 40
- Factors of 31: The factors of 31 are 1 and 31.
- Factors of 32: The factors of 32 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32.
- Factors of 33: The factors of 33 are 1, 3, 11, and 33.
- Factors of 34: The factors of 34 are 1, 2, 17, and 34.
- Factors of 35: The factors of 35 are 1, 5, 7, and 35.
- Factors of 36: The factors of 36 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 36.
- Factors of 37: The factors of 37 are 1 and 37.
- Factors of 38: The factors of 38 are 1, 2, 19, and 38.
- Factors of 39: The factors of 39 are 1, 3, 13, and 39.
- Factors of 40: The factors of 40 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, and 40.
Factors of Numbers 41 to 50
- Factors of 41: The factors of 41 are 1 and 41.
- Factors of 42: The factors of 42 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21, and 42.
- Factors of 43: The factors of 43 are 1 and 43.
- Factors of 44: The factors of 44 are 1, 2, 4, 11, 22, and 44.
- Factors of 45: The factors of 45 are 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, and 45.
- Factors of 46: The factors of 46 are 1, 2, 23, and 46.
- Factors of 47: The factors of 47 are 1 and 47.
- Factors of 48: The factors of 48 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, and 48.
- Factors of 49: The factors of 49 are 1, 7, and 49.
- Factors of 50: The factors of 50 are 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, and 50.
Factors of Numbers 51 to 60
- Factors of 51: The factors of 51 are 1, 3, 17, and 51.
- Factors of 52: The factors of 52 are 1, 2, 4, 13, 26, and 52.
- Factors of 53: The factors of 53 are 1 and 53.
- Factors of 54: The factors of 54 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, and 54.
- Factors of 55: The factors of 55 are 1, 5, 11, and 55.
- Factors of 56: The factors of 56 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 14, 28, and 56.
- Factors of 57: The factors of 57 are 1, 3, 19, and 57.
- Factors of 58: The factors of 58 are 1, 2, 29, and 58.
- Factors of 59: The factors of 59 are 1 and 59.
- Factors of 60: The factors of 60 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30, and 60.
Factors of Numbers 61 to 70
- Factors of 61: The factors of 61 are 1 and 61.
- Factors of 62: The factors of 62 are 1, 2, 31, and 62.
- Factors of 63: The factors of 63 are 1, 3, 7, 9, 21, and 63.
- Factors of 64: The factors of 64 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 64.
- Factors of 65: The factors of 65 are 1, 5, 13, and 65.
- Factors of 66: The factors of 66 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 11, 22, 33, and 66.
- Factors of 67: The factors of 67 are 1 and 67.
- Factors of 68: The factors of 68 are 1, 2, 4, 17, 34, and 68.
- Factors of 69: The factors of 69 are 1, 3, 23, and 69.
- Factors of 70: The factors of 70 are 1, 2, 5, 7, 10, 14, 35, and 70.
Factors of Numbers 71 to 80
- Factors of 71: The factors of 71 are 1 and 71.
- Factors of 72: The factors of 72 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, and 72.
- Factors of 73: The factors of 73 are 1 and 73.
- Factors of 74: The factors of 74 are 1, 2, 37, and 74.
- Factors of 75: The factors of 75 are 1, 3, 5, 15, 25, and 75.
- Factors of 76: The factors of 76 are 1, 2, 4, 19, 38, and 76.
- Factors of 77: The factors of 77 are 1, 7, 11, and 77.
- Factors of 78: The factors of 78 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 13, 26, 39, and 78.
- Factors of 79: The factors of 79 are 1 and 79.
- Factors of 80: The factors of 80 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, 20, 40, and 80.
Factors of Numbers 81 to 90
- Factors of 81: The factors of 81 are 1, 3, 9, 27, and 81.
- Factors of 82: The factors of 82 are 1, 2, 41, and 82.
- Factors of 83: The factors of 83 are 1 and 83.
- Factors of 84: The factors of 84 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 12, 14, 21, 28, 42, and 84.
- Factors of 85: The factors of 85 are 1, 5, 17, and 85.
- Factors of 86: The factors of 86 are 1, 2, 43, and 86.
- Factors of 87: The factors of 87 are 1, 3, 29, and 87.
- Factors of 88: The factors of 88 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 11, 22, 44, and 88.
- Factors of 89: The factors of 89 are 1 and 89.
- Factors of 90: The factors of 90 are 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 15, 18, 30, 45, and 90.
Factors of Numbers 91 to 100
- Factors of 91: The factors of 91 are 1, 7, 13, and 91.
- Factors of 92: The factors of 92 are 1, 2, 4, 23, 46, and 92.
- Factors of 93: The factors of 93 are 1, 3, 31, and 93.
- Factors of 94: The factors of 94 are 1, 2, 47, and 94.
- Factors of 95: The factors of 95 are 1, 5, 19, and 95.
- Factors of 96: The factors of 96 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 32, 48, and 96.
- Factors of 97: The factors of 97 are 1 and 97.
- Factors of 98: The factors of 98 are 1, 2, 7, 14, 49, and 98.
- Factors of 99: The factors of 99 are 1, 3, 9, 11, 33, and 99.
- Factors of 100: The factors of 100 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50, and 100.
Conclusion
Understanding the factors of numbers is crucial for various mathematical operations and provides the foundation for more complex topics such as prime numbers, greatest common divisors (GCD), and least common multiples (LCM). Factors help simplify expressions, solve problems, and understand the relationships between numbers. For numbers 1 to 100, we have covered all the divisors of each number, which are helpful for applications in number theory, algebra, and other areas of mathematics.
By practicing and recognizing the factors of numbers, one can improve their problem-solving skills and mathematical intuition. This knowledge is essential not only in academic contexts but also in real-world applications like cryptography, computer science, and engineering.
Additional Sources
Saad Raza is an SEO specialist with 7+ years of experience in driving organic growth and improving search rankings. Skilled in data-driven strategies, keyword research, content optimization, and technical SEO, he helps businesses boost online visibility and achieve sustainable results. Passionate about staying ahead of industry trends, Saad delivers measurable success for his clients.